LEARNING OBJECTIVES
-
Be able to explain what a network is.
-
Understand and identify the different types of networks.
-
Be able to explain what factors affect the performance of a network.
SUCCESS CRITERIA
Success Criteria:
-
Explain the difference between LAN and WAN.
-
Identify what factors affect the performance of networks.
1.4 Wired and Wireless Networks
Learners should have studied the following:
-
LO1- types of networks:
LAN (Local Area Network)
WAN (Wide Area Network) -
factors that affect the performance of networks
-
the different roles of computers in a client-server and a peer-to-peer network
-
the hardware needed to connect stand-alone computers into a Local Area Network:
wireless access points
routers/switches
NIC (Network Interface Controller/Card)
transmission media -
the internet as a worldwide collection of computer networks:
DNS (Domain Name Server)
hosting the cloud -
the concept of virtual networks.
If you look up the network types online, you will find a huge variety. The main thing to get from this is that networking computers is extremely useful and there will always be new ways to connect computers and new uses found for networks.
Note
EXAM TIP
It's important to understand the different types of networks and where they are used.
KEYWORDS
Interference - additional energy that appears in a network, that causes a signal to be disrupted.
Bottleneck - data that is delayed in transmission through an overload section of a network.
HOME LEARNING
Research 5 other types of networks. Explain the characteristics and give a description for each characteristic.
Create a PowerPoint presentation or do in Microsoft Word.
Due next lesson.
Networks- LESSON 1
Types of networks
KEYWORDS
Stand-alone computer - A computer that is not connected to a network.
Network - A collection of computers that are connected together.
Peripheral - A device that is attached to a computer system.
Network Traffic - The amount of traffic that is travelling across a network at any one time.
Click on the link to access the worksheet for this task.
Networks- Introduction
Up until the 1990's, most computers in both the home and in businesses were stand-alone computers. A stand alone computer is one that is not connected to any other computers that it needs for regular use. When we connect computers together we create a network.
One of the first networks to be created was called Advanced Research Projects Agency Network(ARPANET) in 1969. A group of universities decided to connect their computers together so they could communicate with each other and share resources.
Networks consists of two types of components , nodes and links.
Each device on a network is referred to as a node, these are connected by some means such as cabling or wireless (links).
Inside every computer system, digital signals are moved about between components. Signals are passed as a stream of 0's and 1's between the peripherals and the computer, and between the internal components of the computer. It is no great extension of that mechanism to connect computers together so they can share data and 'talk' to each other.
Most networks are connected, if not to a local area network, then probably to the internet. Even embedded systems are often connected.
Example:
-
Car engine management systems can signal problems online to a central system.
-
Burglar alarm systems can contact controllers.
-
Large installations such as aircraft avionics contain multiple processors all connected to each other.
There are a range of advantages and disadvantages of networking computers together; these include:

LO1 - Types of Networks

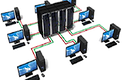
Networks can be classified in various ways such as by their extent, the nature of their components or the nature of their connections.
Classification by extent:
LAN
A LAN is a Local Area Network. This means that the computers and connections are located on one site usually covering a small geographical area. This network might be in a single building or a group of buildings such as a university campus.
The key characteristics of a LAN include:
WAN
A WAN is a wide area Wide Area Network. This typically covers a large geographical area, taking in many cities, often worldwide. The connections are typically provided by a telecoms company. As with a LAN, the users will see a transparent resource, normally not needing to know about where individual computers are located.
The key characteristics of a WAN include:


LO1-Factors that affect the performance of networks
The performance of a network is something that is very important if we want it to be efficient. But what do you mean by the performance? We mean how well the network is operating and how free from errors it is: this includes how quickly data can be transmitted around the network.
There are a number of factors that can affect the performance of a network, including:

